Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law: Understanding Voltage, Current, and Resistance
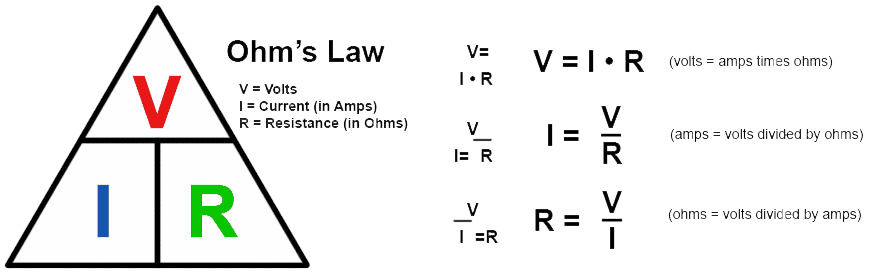
Introduction: Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. It provides a simple mathematical formula to determine one of these quantities when the other two are known. Understanding Ohm's Law is essential for analyzing and designing electrical circuits.
The Formula: Ohm's Law is represented by the formula: V = I × R
- V: Voltage (in volts)
- I: Current (in amperes)
- R: Resistance (in ohms)
Explanation with Examples:
Calculating Voltage (V): If we know the current (I) flowing through a resistor and the resistance (R) of the resistor, we can find the voltage (V) across it. Example: If a resistor has a current of 2 amperes flowing through it and a resistance of 5 ohms, then the voltage across it is: V = I × R V = 2 A × 5 Ω = 10 V
Calculating Current (I): If we know the voltage (V) applied across a resistor and the resistance (R) of the resistor, we can find the current (I) flowing through it. Example: If a resistor with a resistance of 3 ohms is connected to a voltage source of 12 volts, then the current flowing through it is: V = I × R I = V / R I = 12 V / 3 Ω = 4 A
Calculating Resistance (R): If we know the voltage (V) applied across a resistor and the current (I) flowing through it, we can find the resistance (R) of the resistor. Example: If a voltage of 9 volts is applied across a resistor, and it allows a current of 3 amperes to flow through it, then the resistance of the resistor is: V = I × R R = V / I R = 9 V / 3 A = 3 Ω
Conclusion: Ohm's Law is a fundamental tool for understanding and analyzing electrical circuits. By applying this simple relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, we can solve a wide range of problems in electronics and electrical engineering. Whether you're designing circuits, troubleshooting issues, or simply learning about electricity, Ohm's Law is an indispensable concept to master.

Comments
Post a Comment